Is Memcache Still the Cool Cat Worth Your Precious Time and Energy?
Hungry for speed, insatiable for efficiency – in the world of data, the quest for faster access is my unending appetite
The Rise of Memcache
Memcache has been a household name in the world of web development and system optimization for over a decade created by Brad Fitzpatrick. This open-source, in-memory caching system has saved countless web applications from the performance bottlenecks that come with querying databases for repetitive data. Its simplicity, speed, and efficiency made it a go-to solution for many tech professionals.
The New Kids on the Block
In recent years, newer caching solutions like Redis, Varnish, and various CDN (Content Delivery Network) services have entered the scene. These newcomers have brought their own unique features and advantages, and many wonder if Memcache can still hold its own.
A Closer Look at Memcache
To determine if Memcache is still the "cool cat" of caching, we need to assess its strengths and weaknesses:
Strengths
Simplicity: Memcache is straightforward to set up and use. Its basic key-value store design is easy to understand, making it accessible for developers of all levels.
Speed: The in-memory storage ensures lightning-fast data retrieval, reducing the load on your database server and improving your application's responsiveness.
Efficiency: Memcache efficiently handles high read loads and is excellent for caching frequently accessed data.
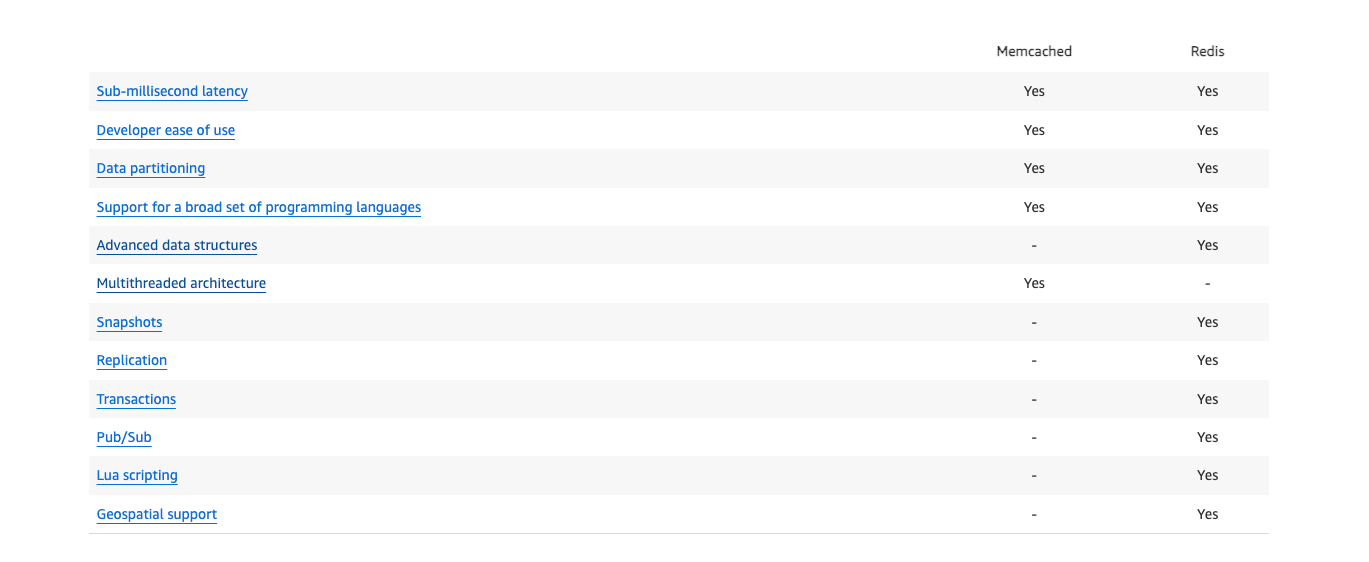
Multithreaded: Memcached’s distributed and multithreaded architecture makes it easy to scale. You can split your data among a number of nodes, enabling you to scale out capacity by adding new nodes to your cluster. Moreover, since Memcached is multithreaded, it can use multiple cores on a given node. This makes it simple to scale up compute capacity. With Memcached you can build highly scalable distributed caching solutions designed to provide fast and consistent performance.
Note - Redis v6.0 added multithreaded architecture too but to tackle network I/O bottleneck
Redis 6.0 introduced multi-threading because its bottleneck was not in memory, but in the network I/O module, which consumed CPU time. Therefore, multi-threading was introduced to handle network I/O and make full use of CPU resources, reducing the performance loss caused by network I/O blocking.
Weaknesses
Limited Features: Memcache primarily serves as a basic cache. It lacks advanced features like data persistence and complex data structures, which other solutions may offer.
Single-Node Failure: Memcache does not inherently provide redundancy or failover options. If your Memcache server goes down, your cached data could be lost.
Key Size Limitation: If your keys in Memcache start creeping beyond the 250-byte mark, you might run into trouble. That's when Redis steps in like a knight in shining armor, ready to handle those extra-long keys with ease.
AWS Elasticache - Memcache vs Redis
Where Redis is the Perfect Cool Cat?
Ah, Redis, the show-off in the world of caching! It just can't resist flexing its data storage muscles over poor Memcache. Why settle for basic caching when you can have Redis's data persistence, sophisticated data structures, and even its own built-in messaging system? Memcache is like the kid riding a bicycle, while Redis is cruising around in a Formula 1 car. So, if you're into making caching as complex and powerful as a superhero's origin story, Redis is the obvious choice. Who needs simplicity when you can have it all, right? 😄
So, Is Memcache Still the Cool Cat Worth Your Precious Time and Energy?
Well, well, Memcached, is the choice of all choices for app developers. Who needs data to last? It's like the here-today-gone-tomorrow rock star of in-memory storage. With its lightning-fast sub-millisecond latency, it's like the Usain Bolt of databases – blink, and your data's gone! But hey, it's your jam if you want to play it fast and loose with user profiles, credentials, and session state. Persistence is so last season! 😄
The Cool Cat references for the Memcache Lovers -
1. Scaling Memcache at Facebook
2. Netflix's EVCache wrapper on Memcache


